When it comes to supporting your digestive health, digestive enzymes and probiotics are two key players. But what exactly sets them apart? In this comprehensive article, we will explore the fascinating differences between digestive enzymes and probiotics, helping you understand how they work and the specific benefits they offer. Whether you're seeking relief from digestive issues or aiming to optimize your gut health, this expert guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about incorporating these supplements into your wellness routine.
What Are Digestive Enzymes?
The body produces digestive enzymes, which are proteins that are essential for breaking down food into smaller, more easily absorbed molecules. The salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine are just a few of the digestive system organs that secrete these enzymes. Each type of digestive enzyme has a specific function, such as breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. By facilitating the digestion and absorption of nutrients, digestive enzymes help optimize the body's nutrient uptake and support overall digestive health.
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms, typically bacteria or yeasts, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These beneficial bacteria are naturally found in the human gut and can also be obtained through certain foods or supplements. Probiotics work by colonizing the gut and promoting a healthy balance of bacteria, which is essential for proper digestion and immune function. They can help improve the diversity and abundance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, while inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. Probiotics have been associated with various health benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and even mental well-being. Incorporating probiotics into your diet can be a proactive way to support your overall health and well-being.
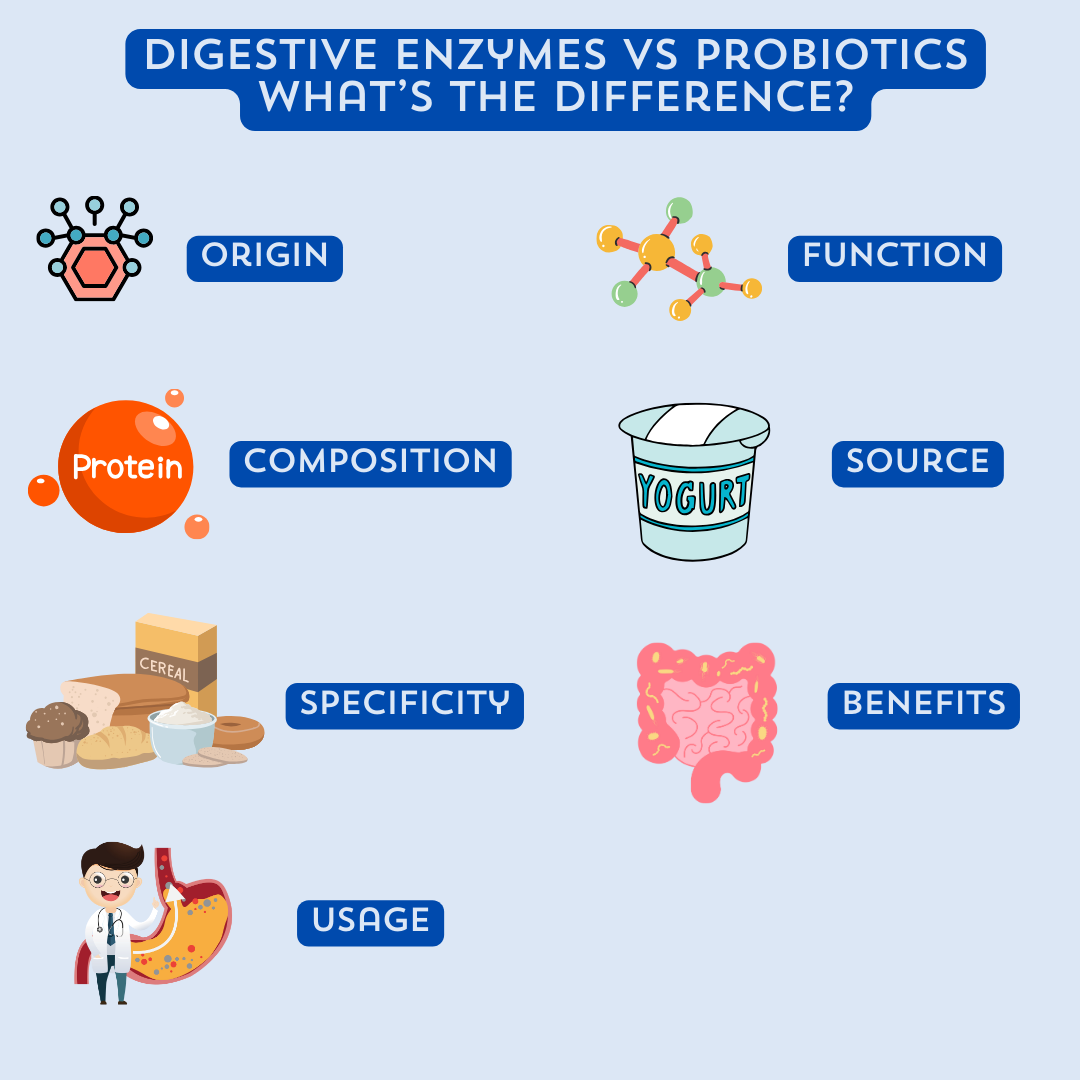
Digestive Enzymes vs Probiotics What’s The Difference?
Here are the key differences between digestive enzymes and probiotics:
- Origin: The body naturally produces digestive enzymes, whereas probiotics are live microorganisms that are available through specific foods or supplements.
- Function: Digestive enzymes play a vital role in breaking down food into smaller molecules for better absorption, while probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut and support overall digestive health.
- Composition: Digestive enzymes are proteins, whereas probiotics are typically bacteria or yeasts.
- Source: The salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine are just a few of the digestive system's organs that secrete digestive enzymes. Probiotics can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi, as well as in probiotic supplements.
- Specificity: Digestive enzymes have specific functions, such as breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Probiotics, on the other hand, work by promoting a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut and do not have specific digestive functions.
- Benefits: Digestive enzymes aid in digestion and nutrient absorption, while probiotics support gut health, immune function, and may offer additional benefits like improved mental well-being.
- Usage: Digestive enzymes are often taken with meals to support digestion, while probiotics are typically taken on a regular basis to maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
Understanding these differences can help you determine whether you may benefit from incorporating digestive enzymes or probiotics into your wellness routine.
Which Is Better For Digestive Support Digestive Enzymes vs Probiotics?
Determining whether digestive enzymes or probiotics are better for digestive support depends on individual needs and goals. Digestive enzymes are beneficial for individuals who struggle with specific digestive issues or have difficulty breaking down certain types of food and nutrients. They can aid in digestion and nutrition absorption. On the other hand, probiotic benefits are advantageous for those looking to maintain a healthy gut microbiome and support overall gut health. They promote a balanced gut bacteria population and can help with digestive issues related to an imbalance in gut flora. Ultimately, the choice between digestive enzymes and probiotics depends on the specific digestive concerns and goals of each individual. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance to determine which option may be more suitable for optimal digestive support.
What Are The Pros and Cons Of Digestive Enzymes vs Probiotics?
Pros and Cons of Digestive Enzymes
Pros:
- Improved Digestion: Digestive enzymes can enhance the breakdown of food, leading to improved digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Relief from Digestive Issues: Digestive enzymes may help alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders, such as bloating, gas, and indigestion.
- Support for Specific Dietary Needs: Certain digestive enzymes, like lactase, can assist individuals with lactose intolerance in digesting dairy products.
- Convenience: Digestive enzyme supplements are widely available and can be easily incorporated into your daily routine.
Cons:
- Limited Effectiveness for Some Conditions: Digestive enzymes may not provide significant benefits for certain digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Potential Side Effects: In some cases, digestive enzyme supplements may cause mild side effects like stomach upset, diarrhea, or allergic reactions.
- Cost: High-quality digestive enzyme supplements can be expensive, especially if long-term use is required.
- Dependency: There is a concern that long-term use of digestive enzyme supplements may lead to dependency, as the body may become reliant on external sources of enzymes.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, including digestive enzymes, to determine if they are suitable for your specific needs and to discuss potential risks or interactions with other medications.
Pros and Cons of Probiotics
Pros:
- Improved Gut Health: Probiotics can help restore and maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut, which is essential for optimal digestion and overall gut health.
- Enhanced Immune Function: Certain strains of probiotics have been shown to support immune function and may help reduce the risk of respiratory and gastrointestinal infections.
- Potential Mental Health Benefits: Emerging research suggests that probiotics may have a positive impact on mental well-being, potentially improving symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Availability: Probiotics can be obtained through fermented foods or easily accessed in the form of supplements.
Cons:
- Strain-Specific Effects: Different strains of probiotics may have varying effects, and not all strains have been extensively studied or proven effective for specific health conditions.
- Individual Variability: The response to probiotics can vary from person to person, and what works for one individual may not work for another.
- Potential Digestive Discomfort: Some individuals may experience temporary digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas, when starting probiotics. This usually subsides as the body adjusts.
- Quality and Storage: The quality and viability of probiotics can vary, and proper storage conditions are necessary to maintain their effectiveness.
As with any supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable probiotic strain, dosage, and duration of use based on your individual health needs and goals.
What Foods Are High In Probiotics?
Several foods are rich in probiotics and can be incorporated into your diet to increase your intake of these beneficial microorganisms. Fermented foods are particularly high in probiotics. Examples include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh, miso, and kombucha. Yogurt and kefir, in particular, contain strains of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Additionally, certain types of cheese, such as Gouda and cheddar, can also contain probiotic strains. When selecting probiotic-rich foods, it is important to choose options that are labeled as containing live and active cultures to ensure the presence of beneficial bacteria. Incorporating these foods into your diet can be a delicious way to support your gut health and increase your probiotic intake.
Are High Fat and Bitter Foods Harder To Digest?
High fat and bitter foods can be more challenging for the digestive system to process compared to other types of foods. High-fat foods, such as fried foods or fatty cuts of meat, require more time and effort for the body to break down and digest due to their complex composition. The presence of fat can slow down the digestive process and may lead to feelings of heaviness or discomfort. Bitter foods, on the other hand, can stimulate the production of digestive juices and enzymes, aiding in digestion. However, some individuals may find bitter flavors less palatable, which can affect their overall enjoyment of the meal and potentially impact digestion. It is important to note that individual tolerance and digestive capacity can vary, so it is advisable to listen to your body and make dietary choices that align with your personal needs and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between digestive enzymes and probiotics is essential for individuals seeking to optimize their digestive health. Digestive enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down food and aiding in nutrient absorption, while probiotics support a healthy balance of gut bacteria and overall gut health. Both supplements offer unique benefits and can be valuable additions to a wellness routine. Digestive enzymes can be particularly beneficial for those with specific digestive issues or difficulty digesting certain foods, while probiotics are advantageous for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Ultimately, the choice between digestive enzymes and probiotics depends on individual needs and goals. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance to determine the most suitable option for optimal digestive support. By incorporating these supplements and making informed choices, individuals can take proactive steps towards enhancing their digestive well-being and overall health.
Final Thoughts
Discover enhanced well-being with Vitalzym Extra Strength. This World Nutrition enzyme supplement, packed with papain from papaya, boosts enzyme levels, strengthens immunity, and supports fast recovery and circulation. Featuring serrapeptase and bromelain, Vitalzym is your path to a healthier life. Tap into the power of papaya with Vitalzym today.*
Sources
- https://www.kefirwala.in/what-is-bifidobacterium-how-to-get-it
- https://www.avogel.co.uk/health/digestive-system/are-you-struggling-to-digest-fats/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2024/01/10/are-probiotic-supplements-worth-the-money-gut-health-expert-weighs-in.html
- https://www.theguardian.com/society/2021/jul/11/unlocking-the-gut-microbiome-and-its-massive-significance-to-our-health
These statements have not been evaluated by the food and drug administration (FDA). These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.