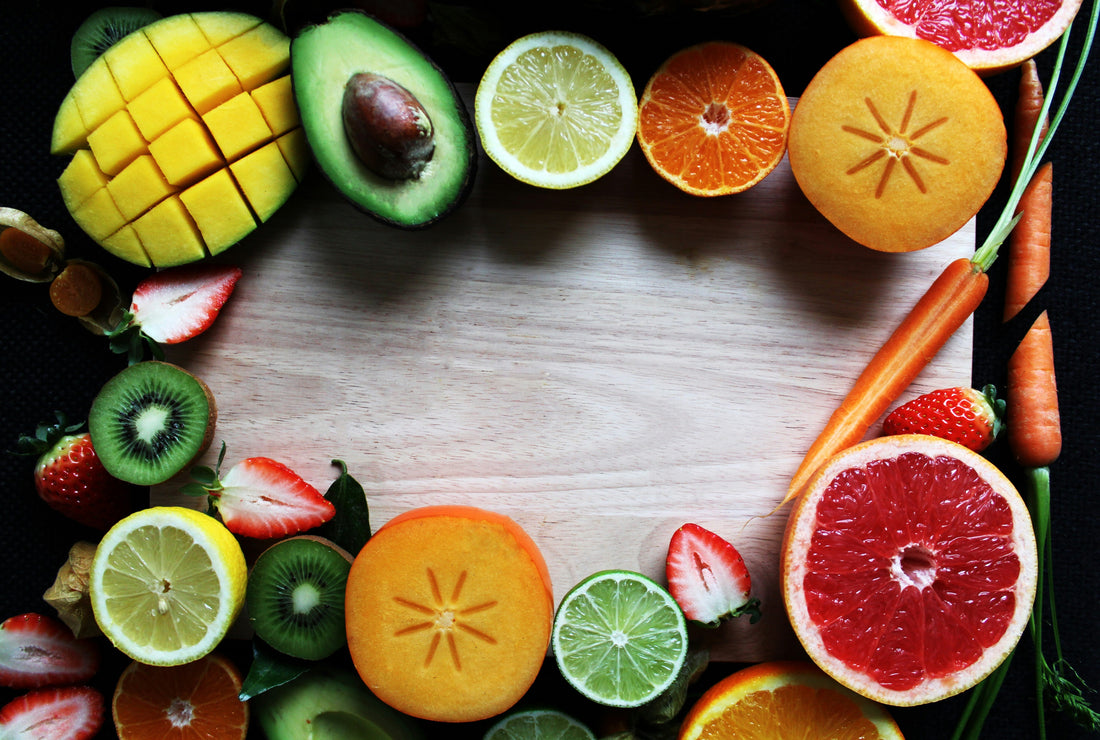
Are you struggling with digestive issues and looking for relief? In this article, we will explore the top foods that are easy to digest, helping you manage symptoms and improve your overall well-being. Whether you suffer from irritable bowel syndrome, acid reflux, or chronic indigestion, our expert recommendations will provide you with the knowledge and confidence to make informed dietary choices. Discover the top picks that will keep your stomach happy and your body nourished, allowing you to enjoy meals without the worry of discomfort.
Why Are Some Foods Harder To Digest?
Digestion is a complex process that involves breaking down food into smaller molecules for absorption and utilization by the body. Some foods can be harder to digest due to their composition or certain factors that affect the digestive system. For example, foods high in fat or fiber take longer to break down, requiring more digestive enzymes and time for processing. Additionally, certain foods, such as beans or cruciferous vegetables, contain compounds that can cause gas or bloating in some individuals. Moreover, underlying digestive conditions like irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease can make the digestion of certain foods more challenging. Understanding why some foods are harder to digest can help individuals with digestive issues make informed dietary choices to manage their symptoms effectively.
Common Foods Causing Gut Health and Abdominal Pain Issues
- Spicy Foods: Spicy foods can trigger gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea in some individuals. If you experience discomfort after consuming spicy foods, it may be helpful to reduce your intake or avoid them altogether. Consulting with a gastroenterologist or dietitian can provide further guidance.
- Fatty Foods: High-fat foods, especially those that are deep-fried or greasy, can be difficult to digest and may lead to abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. Limiting your intake of fatty foods can help alleviate these symptoms and reduce inflammation in the gut.
- Dairy Products: Some individuals may have lactose intolerance, which can cause abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and nausea after consuming dairy products. If you suspect lactose intolerance, try reducing or eliminating dairy from your diet and consider alternative options like lactose-free products or dairy substitutes.
- Gluten-Containing Foods: For individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, consuming gluten-containing foods can trigger abdominal pain, diarrhea, and inflammation in the gut. It is important to work with a gastroenterologist or dietitian to properly diagnose and manage these conditions through a gluten-free diet.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Certain artificial sweeteners, such as sorbitol and xylitol, can have a laxative effect and cause gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. Pay attention to food labels and consider reducing or avoiding products that contain these sweeteners if you experience digestive issues.
- Carbonated Beverages: Carbonated beverages, including soda and sparkling water, can cause gas and bloating, leading to abdominal discomfort. Opting for still water or non-carbonated drinks may help alleviate these symptoms.
- High-Fiber Foods: While fiber is generally beneficial for gut health, consuming excessive amounts of high-fiber foods, especially if you're not accustomed to them, can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. Gradually increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated can help prevent these issues.
It is important to note that individual tolerances and sensitivities can vary. If you experience persistent or severe gut health issues and abdominal pain, it is recommended to consult with a gastroenterologist and/or a registered dietitian for proper evaluation and personalized guidance.
What Foods Are Easy To Digest?
Lean Proteins: A Gentle Source of Nutrition
Lean proteins are excellent options for easy digestion. Foods such as skinless chicken, turkey, fish, and tofu are low in fat and tend to be well-tolerated by the digestive system. These proteins provide essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth without putting excessive strain on the digestive organs. Opt for grilled, baked, or steamed preparations to keep them light and easily digestible.
Fiber-Rich Foods: Supporting Digestion without Discomfort
While some high-fiber foods can be challenging to digest, there are plenty of options that are gentle on the stomach. Easy fiber foods like cooked vegetables like carrots, spinach, and zucchini are easier to break down compared to their raw counterparts. Fruits like bananas and melons are also well-tolerated due to their softer texture. Incorporating soluble fiber sources like oats and chia seeds can help support gut health and regulate bowel movements without causing digestive distress.
Gut-Friendly Fruits and Vegetables: Nourishing and Soothing
Certain fruits and vegetables have natural properties that promote digestive health. Papaya and pineapple contain enzymes (papain and bromelain, respectively) that aid in gut health and digestion. Cooked or steamed vegetables like sweet potatoes, squash, and green beans are gentle on the stomach. Additionally, leafy greens such as spinach and kale provide essential nutrients while being easy to digest when cooked.
Healthy Fats: Essential for Digestive Health
Not all fats are hard to digest. Opt for sources of healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which are generally well-tolerated by the digestive system. These fats provide essential fatty acids that support overall gut health and can help lubricate the digestive tract. However, it's important to consume them in moderation, as excessive fat intake can lead to discomfort and digestive issues.
Hydration: The Key to a Happy Digestive System
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining proper digestion. Water helps soften and break down food, making it easier to pass through the digestive tract. Additionally, drinking enough fluids prevents constipation and promotes regular bowel movements. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day and consider incorporating hydrating foods like cucumbers and watermelon into your diet.
By incorporating these easy-to-digest foods into your diet, you can support your digestive system and manage symptoms more effectively. Remember to listen to your body and make adjustments based on your individual needs and tolerances.

What Is The Simplest Food To Digest?
The simplest food to digest is often considered to be broth or clear liquids. These include clear soups, bone broth, herbal teas, and electrolyte solutions. These liquids require minimal digestion as they are already in a liquid form and contain few solid components. They provide hydration and some essential nutrients without putting a significant strain on the digestive system. Clear liquids are often recommended during periods of illness, after surgery, or when recovering from digestive issues as they are gentle on the stomach and easily absorbed by the body.
Is Peanut Butter Easy To Digest?
Peanut butter can be relatively easy to digest for many individuals. It contains healthy fats and protein, which are essential for the body's functioning. However, some people with sensitive digestive systems or specific conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or diverticulitis, may find peanut butter difficult to digest due to its high-fat content. Additionally, some individuals may have allergies or intolerances to peanuts, which can cause digestive discomfort. It is important to listen to your body and pay attention to any adverse reactions when consuming peanut butter or any other food.
How To Support Food Digestion
To support food digestion, consider the following strategies:
- Eat Mindfully: Take your time to chew your food thoroughly and savor each bite. Eating slowly allows your body to properly break down the food and signals to your brain when you're full.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Water helps soften food and aids in the digestion process. Aim to drink water between meals rather than during meals to avoid diluting stomach acid.
- Include Fiber-Rich Foods: Incorporate high-fiber foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes into your diet. Fibre adds bulk to the stool, promotes regular bowel movements, and supports overall digestive health.
- Consume Probiotic-Rich Foods: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can aid in digestion. Include fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi in your diet to promote a healthy gut microbiome.
- Consider Digestive Enzyme Supplements: Digestive enzyme supplements can assist in breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, especially for individuals with conditions like pancreatic insufficiency or enzyme deficiencies. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if these supplements are appropriate for you.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact digestion. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in activities that help you relax.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods that trigger digestive discomfort or symptoms. Common culprits include spicy foods, fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated beverages. Keep a food diary to track your reactions to different foods.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help stimulate digestion and promote bowel regularity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Remember, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance on supporting your specific digestive needs.
Is White Rice Easy To Digest?
Yes, white rice is generally considered easy to digest. During the refining process, the outer husk, bran, and germ of the rice grain are removed, leaving behind the starchy endosperm. This makes white rice less fibrous and easier for the body to break down and absorb. The absence of fiber and the softer texture of cooked white rice contribute to its ease of digestion. However, individuals with certain digestive conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or celiac disease, may still experience discomfort or intolerance to white rice. It's important to listen to your body and make dietary choices based on your individual needs and tolerances.
What High Protein and Nutrition Foods Are Easy To Digest?
- Lean Meats: Lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and fish (like salmon or cod) are excellent sources of high-quality protein that are generally easy to digest. Opt for grilled, baked, or steamed preparations to keep them light and easily digestible.
- Eggs: Eggs are a versatile and easily digestible source of protein. They contain all the essential amino acids and can be prepared in various ways to suit individual preferences.
- Greek Yogurt: Greek yogurt is a protein-rich food that also contains beneficial probiotics. It is generally easier to digest compared to other dairy products due to the fermentation process that breaks down lactose.
- Tofu: Tofu is a plant-based protein source made from soybeans. It is low in fat and easy to digest. Tofu can be incorporated into various dishes, such as stir-fries or salads, to boost protein intake.
- Cottage Cheese: Cottage cheese is a soft and easily digestible cheese that is also high in protein. It is lower in lactose compared to other dairy products, making it more tolerable for individuals with lactose intolerance.
- Smoothies with Protein Powder: Adding protein powder to smoothies can be a convenient way to increase protein intake. Opt for high-quality protein powders like whey, pea, or soy protein, which are generally well-tolerated and easily digestible.
- Nut Butters: Nut butters like almond butter or peanut butter are not only rich in protein but also provide healthy fats. They are generally easy to digest, but individuals with nut allergies or sensitivities should exercise caution.
- Quinoa: Quinoa is a gluten-free grain that is high in protein and easy to digest. It is a complete protein source, meaning it contains all essential amino acids. Quinoa can be used as a base for salads, side dishes, or as a substitute for rice or pasta.
- Lentils: Lentils are legumes that are rich in protein and fiber. They are generally well-tolerated and easy to digest. Lentils can be cooked and added to soups, stews, or salads for a nutritious and protein-packed meal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding which foods are easy to digest is crucial for individuals with digestive issues seeking relief and improved gut health. Incorporating lean proteins, fiber-rich foods, gut-friendly fruits and vegetables, healthy fats, and staying hydrated can support digestion and manage symptoms effectively. It is important to listen to your body, identify trigger foods, and make dietary choices based on your individual needs and tolerances. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist or registered dietitian, can provide personalized guidance and ensure optimal digestive health. By making informed choices and prioritizing easy-to-digest foods, individuals can take control of their digestive well-being and experience improved quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Experience the benefits of Vitalzym Extra Strength, the ultimate vegetarian systemic enzyme supplement by World Nutrition. Designed to unlock your body's full potential, this meticulously crafted formula replenishes enzymes, strengthens immune health, accelerates recovery after exercise, and improves circulation. Enriched with a powerful combination of serrapeptase, bromelain, papain, and other potent ingredients, Vitalzym is your passport to a life of vitality and well-being. Embrace a vibrant and healthier lifestyle with World Nutrition products and discover the remarkable benefits for yourself.*
Sources
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactose_intolerance
- https://www.wku.edu/news/articles/index.php?view=article&articleid=2368
- https://chwbonline.com/top-10-health-benefits-lean-protein/
- https://www.helpguide.org/articles/healthy-eating/choosing-healthy-fats.htm
- https://www.chop.edu/health-resources/food-medicine-clear-liquid-diet
- https://rice-processing.com/rice-processing-steps-from-pre-planting-to-post-production.html
These statements have not been evaluated by the food and drug administration (FDA). These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.